
NovorIdfileReader clearTagsMap() - Method in class .io.identifications.idfilereaders. MzIdentMLIdfileReader clearTagsMap() - Method in class .io.identifications.idfilereaders. MsAmandaIdfileReader clearTagsMap() - Method in class .io.identifications.idfilereaders.

DirecTagIdfileReader clearTagsMap() - Method in class .io.identifications.idfilereaders. AndromedaIdfileReader clearTagsMap() - Method in class .io.identifications.idfilereaders. clearTagsMap() - Method in class .io.identifications.idfilereaders. In addition, we expect that the active and collaborative community of Galaxy users and developers will continue to add to the proteogenomic resource described here.Clears the tags map. Although not the focus here, Galaxy-based tools for quantifying RNA-Seq and MS-based proteomics data are available for quantitative proteogenomic analysis. Adding functionality for converting PSM information to a SAM file ( 7) for downstream viewing in the Integrated Genomics Viewer (/software/igv) are also in progress. We are also working on a Galaxy plugin for visualizing proteogenomic results, enabling further viewing of PSM and protein identifications. For example, customized workflows for multi-stage database searching to facilitate variant-specific FDR estimates ( 1) are being developed. The resource described here provides foundational tools and workflows for proteogenomics analysis, implemented in the extensible Galaxy platform to facilitate further enhancements. Sequence database searching and variant confirmation workflow
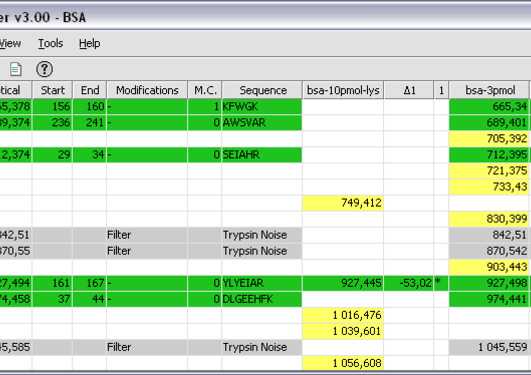
We have developed workflows (accessed through z.umn.edu/canresgithub) for analyzing single-end RNA-Seq data (from a mouse sample) and also for paired-end RNA-Seq data (from human MCF7 cells). The possible variant sequences are merged with reference protein sequences for the organism being studied to create a comprehensive sequence database for the sample being studied. FASTA format, which contains potential variant protein sequences, and annotation for the type of variant (e.g., SAV, Indel). CustomProDB creates a customized protein sequence database in the common.

VCF file acts as an input to the tool CustomProDB ( 11). BAM file (RNA sequence alignment information), the. These tools generate a variant call format (.VCF) file that provides a summary of all potential variants identified from the starting RNA-Seq data. The current workflow focuses on insertion-deletion (Indel) variants and single amino acid variants (SAV).
#Compomics searchgui series
The workflow's input is raw RNA-Seq data (.FASTQ) along with a genomic annotation file (.GTF), which are analyzed by a series of tools to identify and assemble potential sequence variants from these data.
#Compomics searchgui software
This workflow, in part, takes advantage of well-documented, mature software for RNA-Seq data analysis that are long-standing, core tools in the Galaxy platform. Directions for accessing software tools and workflows, along with instructional documentation, can be found at z.umn.edu/canresgithub. Our resource brings together software from several leading research groups to address two foundational aspects of proteogenomics: (i) generation of customized, annotated protein sequence databases from RNA-Seq data and (ii) accurate matching of tandem mass spectrometry data to putative variants, followed by filtering to confirm their novelty.
To address this need, we have developed an extensible, Galaxy-based resource aimed at providing more researchers access to, and training in, proteogenomic informatics. This approach is computationally intensive, requiring integration of disparate software tools into sophisticated workflows, challenging its adoption by nonexpert, bench scientists. Proteogenomics has emerged as a valuable approach in cancer research, which integrates genomic and transcriptomic data with mass spectrometry–based proteomics data to directly identify expressed, variant protein sequences that may have functional roles in cancer.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
